Qseed
This page covers the Qseed application architecture that downloads quantum entropy from Qrypt’s entropy service and injects it into a PKCS#11 compliant HSM (Hardware Security Modules) as seed random.
This service requires an access token. Please contact us to obtain one.
Technology Value
Many of the available HSMs use non-quantum entropy sources. Fortunately, the PKCS#11 Cryptoki interface provides a C_SeedRandom function to inject entropy into a PKCS#11 compliant HSM. Developers can inject Qrypt’s quantum entropy into a HSM using the C_SeedRandom function. As a result, HSM keys can be pseudorandomly generated from quantum entropy.
Overview
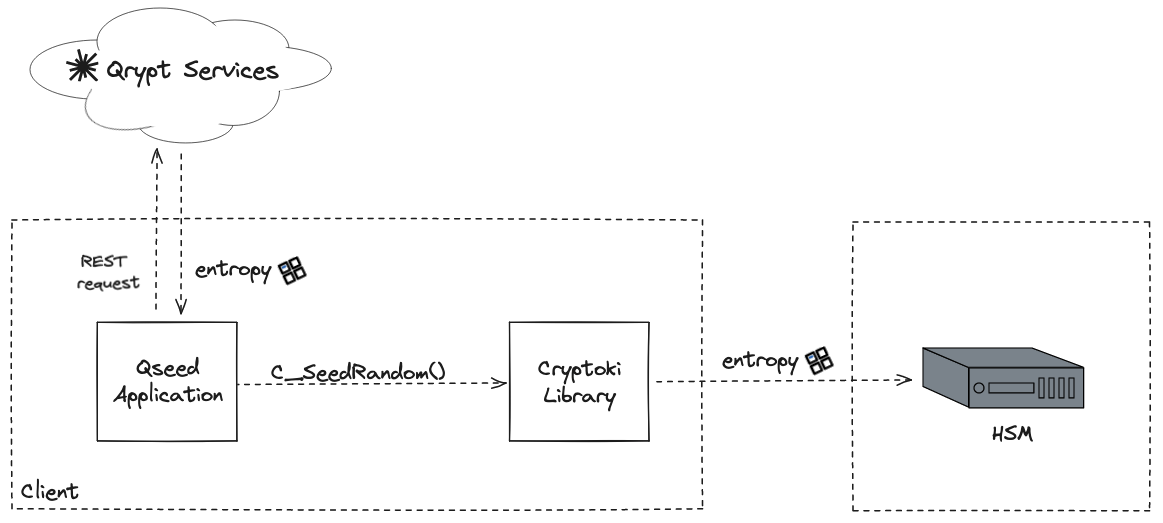
There are four components to the architecture diagram above.
- Qrypt Services: Qrypt’s entropy service that can provide quantum entropy via a REST API.
- Qseed Application: Application that periodically retrieves entropy from Qrypt’s entropy service and injects it into an HSM via a PKCS#11 Cryptoki interface (C_SeedRandom).
- Cryptoki Library: A library that the HSM vendor provides that implements the PKCS#11 Cryptoki interface for their device.
- HSM: Cryptographic hardware or software device.
Installing Qseed Application
The Qseed application and steps to install it can be found here.
Qseed FAQs
How do I inject entropy into multiple HSM partitions?
The Qseed application can only inject entropy into a single partition. In order to seed multiple partitions, you will need to start multiple instances of the Qseed application.
What is the recommended amount of entropy to inject into the HSM?
The Qseed application injects 48 bytes by default. This is recommended for Thales Network Luna 7 HSMs.
Why is more entropy downloaded than injected?
Qrypt’s entropy service supports entropy download at the granularity of KiBs. Extra downloaded entropy is discarded by the Qseed application.
How do I authenticate with the HSM partition using the Security Officer (SO) PIN?
The Qseed application only support Crypto User PINs. You will need to create a Crypto User PIN for the Qseed application.
References
More information about the PKCS#11 Cryptoki interface can be found at Oasis PKCS#11 Specification.